-
[자료구조] HeapArchive/CS & App 2021. 5. 30. 22:41
자료구조 06 / Heap
정의
정의
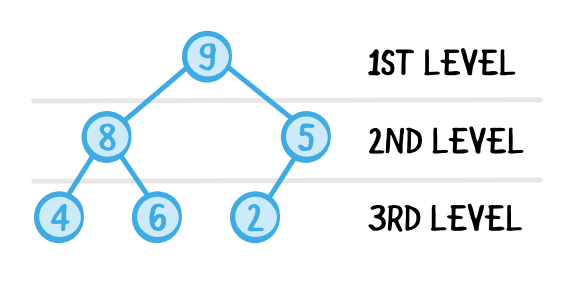
Heap 구조 / Reference : https://www.raywenderlich.com/586-swift-algorithm-club-heap-and-priority-queue-data-structure Heap : 데이터에서 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾는 완전 이진트리 구조 (Complete Binary Tree)
* 완전 이진트리 : Node를 삽입 할때 최하단 왼쪽 Node 부터 차례대로 삽입
힙의 기능
일반적으로 최대값, 최소값을 찾을때 기대값 O(n)
힙에 데이터를 넣는다면 O(logn)
최대값 또는 최소값을 빠르게 찾아야 하는 자료구조 및 알고리즘 구현등에 활용
구조
Max Heap 구조
1) 각 노드의 값은 해당 노드의 자식노드가 가진 값 보다 크거나 같음
2) 완전 이진트리 형태
Min Heap 구조
1) 각 노드의 값은 해당노드의 자식노드가 가진 값보다 작거나 같음
2) 완전 이진트리 형태
구현
배열을 이용한 Heap 구현
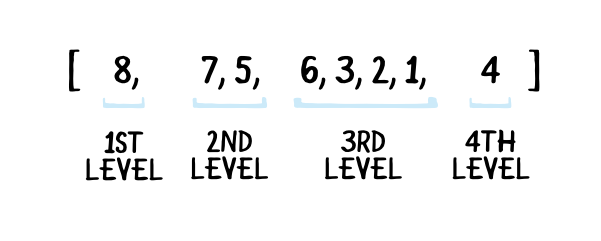
배열을 이용한 Heap 구현 / Reference : https://www.raywenderlich.com/586-swift-algorithm-club-heap-and-priority-queue-data-structure 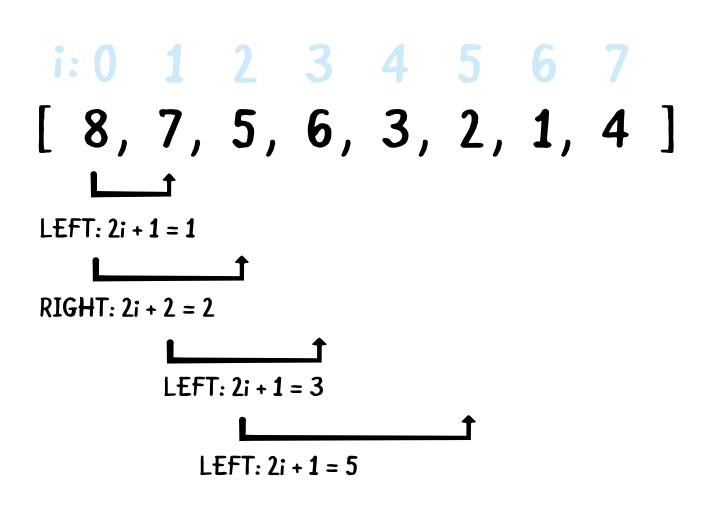
일반적으로 배열로 구현 (완전 이진트리 형태라서 가능)
부모Node index = 자식Node index - 1 / 2
Left자식 index = 부모Node index * 2 + 1
Right 자식 index = 부모Node index * 2 + 2
Implementing a Swift Heap
struct Heap<Element> { var elements : [Element] let priorityFunction : (Element, Element) -> Bool }힙을 배열(완전이진트리)로 표현, 두 요소중 앞에 요소가 더 큰경우 true
Simple functions
extension Heap<Element> { var isEmpty : Bool { return elements.isEmpty } var count : Int { return elements.count } func peek() -> Element? { return elements.first } func isRoot(_ index: Int) -> Bool { return (index == 0) } func leftChildIndex(of index: Int) -> Int { return (2 * index) + 1 } func rightChildIndex(of index: Int) -> Int { return (2 * index) + 2 } func parentIndex(of index: Int) -> Int { return (index - 1) / 2 } }Comparing priority
extension Heap<Element> { // Comparing priority func isHigherPriority(at firstIndex: Int, than secondIndex: Int) -> Bool { return priorityFunction(elements[firstIndex], elements[secondIndex]) } func highestPriorityIndex(of parentIndex: Int, and childIndex: Int) -> Int { guard childIndex < count && isHigherPriority(at: childIndex, than: parentIndex) else { return parentIndex } return childIndex } func highestPriorityIndex(for parent: Int) -> Int { let higherBetweenParentAndLeft = highestPriorityIndex(of: parent, and: leftChildIndex(of: parent)) return highestPriorityIndex(of: higherBetweenParentAndLeft, and: rightChildIndex(of: parent)) } mutating func swapElement(at firstIndex: Int, with secondIndex: Int) { guard firstIndex != secondIndex else { return } swap(&elements[firstIndex], &elements[secondIndex]) } }Enqueueing a new element
mutating func enqueue(_ element: Element) { elements.append(element) siftUp(elementAtIndex: count - 1) } mutating func siftUp(elementAtIndex index: Int) { let parent = parentIndex(of: index) // 1 guard !isRoot(index), isHigherPriority(at: index, than: parent) else { return } // 2, 3 swapElement(at: index, with: parent) // 4 siftUp(elementAtIndex: parent) // 5 }1. 부모 인덱스 / 2. 해당 인덱스가 루트 (0) 인지 확인 / 3. 부모노드 보다 수가 크면 return
4. 자식노드가 더 크므로 부모노드와 자식노드 Swap -> 5. 부모노드에서 다시 확인
Dequeueing the highest priority element
mutating func dequeue() -> Element? { guard !isEmpty else { return nil } swapElement(at: 0, with: count - 1) // 2 let element = elements.removeLast() // 3 if !isEmpty { // 4 siftDown(elementAtIndex: 0) // 5 } return element // 6 } mutating func siftDown(elementAtIndex index: Int) { let childIndex = highestPriorityIndex(for: index) // 1 if index == childIndex { return } // 2 swapElement(at: index, with: childIndex) // 3 siftDown(elementAtIndex: childIndex) }Main
var heap = Heap(elements: [3, 2, 8, 5, 0], priorityFunction: >)'>' Maxheap / '<' Minheap
Build()
extension Heap<Element> { init(elements: [Element] = [], priorityFunction: @escaping (Element, Element) -> Bool) { self.elements = elements self.priorityFunction = priorityFunction // 3 buildHeap() // 4 } mutating func buildHeap() { for index in (0 ..< count / 2).reversed() { // 5 siftDown(elementAtIndex: index) // 6 } }결론
이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree) & Heap (완전 이진 트리)
공통점 : 모두 Binary Tree
차이점 : Heap <> Binart Search Tree
1. 자식노드가 어떤게 클지 알 수 없음 (추가되는 순서) <> 자식노드 왼쪽이 오른쪽 보다 작은 값
2. 최대 / 최소값 검색을 위한 구조 <> 탐색을 위한 구조
시간 복잡도
트리의 높이 death, h
n개의 노드를 가지는 Heap에 데이터 삽입 또는 삭제 시,
최악 root 노드에서 leaf 노드까지 비교 h = log₂n -> O(logn)
구현 코드 : raywenderlich.com
'Archive > CS & App' 카테고리의 다른 글
[자료구조] Graph - 그래프 탐색 방법 (0) 2021.06.26 [자료구조] Graph - 그래프 개념, 인접행렬, 인접리스트 구현 (0) 2021.06.26 [Function] isPrime - 소수판별 (0) 2021.05.17 [자료구조] Tree - AVL Tree (0) 2021.05.06 [자료구조] Tree - Binary Search Tree (0) 2021.05.06